A router connects multiple networks with each other, so that computers from 2 or more different networks can communicate with each other.
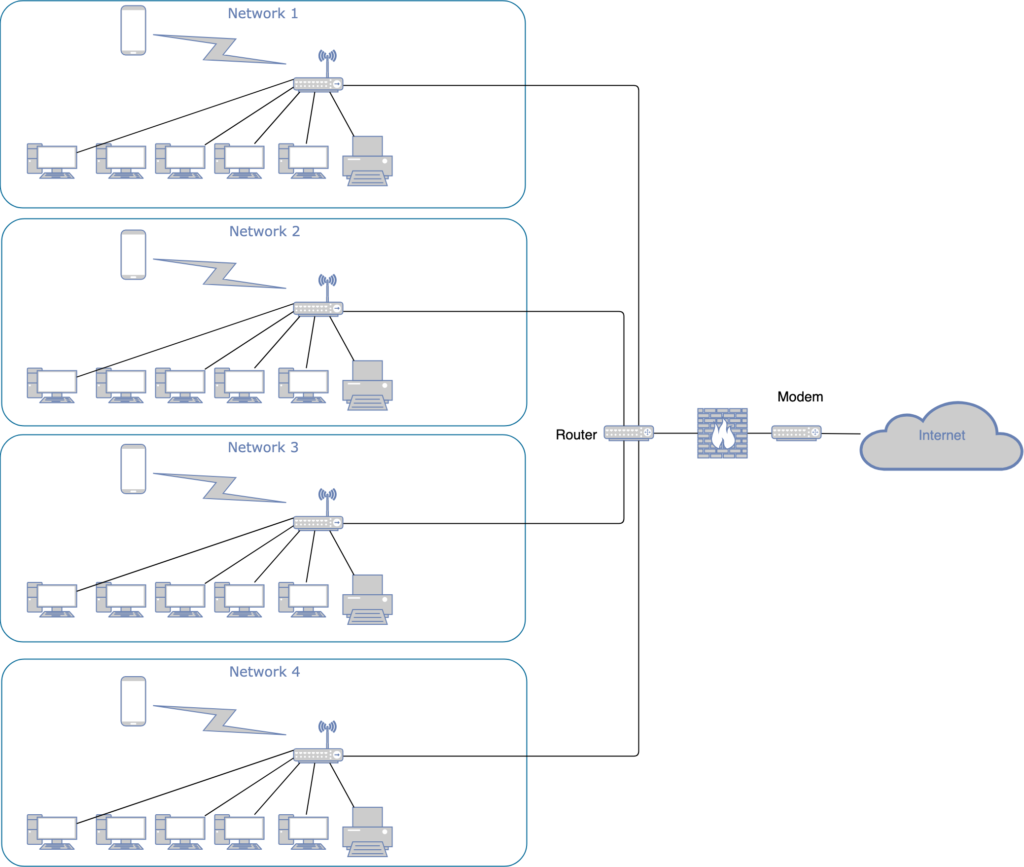
In the example above every computer in network 1 to 4 can communicate with each other and/or the internet (dependent on how the router is configured).
Router “work” in the 3 layer of the OSI model (“Network Layer”). Information like IP-addresses of the sender and recipient, Time-To-Live or protocol typ are present in this layer..
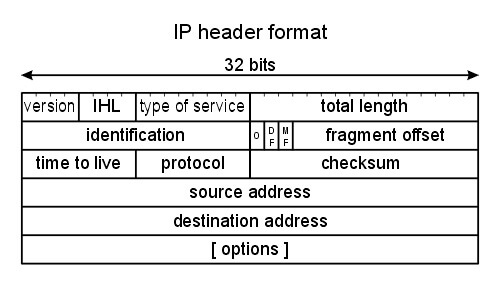
The router knows which packets should be sent through which interface due to the IP address of the sender and recipient.
What are WAN and LAN?
Since multiple networks are connected to a router we have to determine which of these networks are “local” and which are “wide”.
Thats why we have a “Wide Area Network” (WAN), which describes a global network area, and a “Local Area Network” (LAN), which describes a private network area.
Most of the time a router has a specially marked “WAN”-Port, which is usually used for the incoming internet connection.
Example
LAN networks: Your home, company, school
WAN network: The whole network present in the world
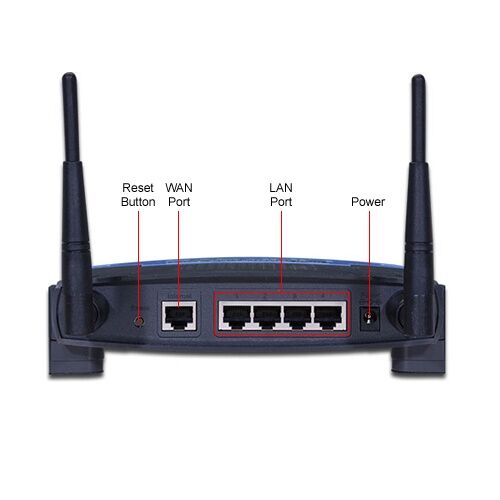

The WAN-Port is used for an incoming internet connection and the LAN-Ports are used for your clients and/or more routers or switches which define your local network structure.
Many routers integrate a modem, which basically handles the authentication to your “Internet-Service-Provider” (ISP).
But some ISPs use a separate device as a modem.
