Table of Contents
Init
Command: git init
Creates a GIT repository in the current working directory.
Status
Command: git status
Compares the current state of the local repository (=commited) with the current state of the file system.
If difference have been found these will be shown as:
- Untracked files
- Files which have not been added to the repository at any time
- Changes not staged for commit
- Here we have 2 categories
- “modified”: Already present files in the repository have been changed
- “deleted”: Already present files in the repository have been deleted
Add
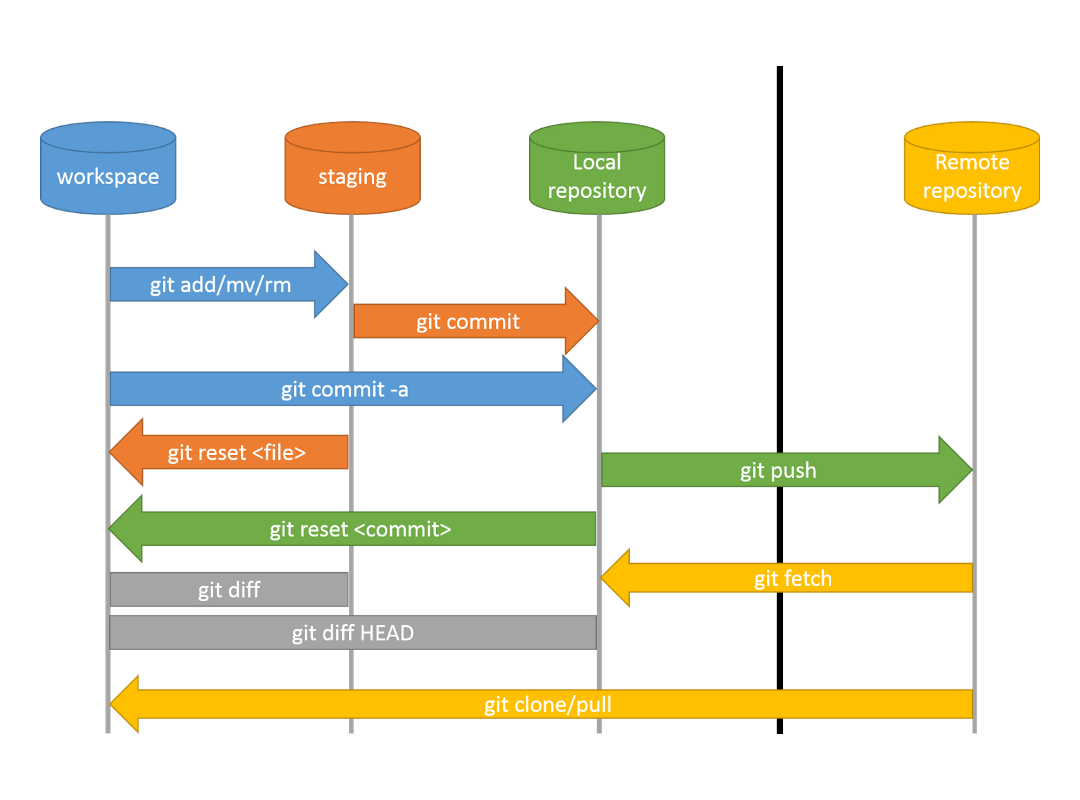
Command: git add <filename> <foldername> <other-things>
Adds given folders and/or files to the “staging”.
This “staging” kann be finally added to the repository via a “git commit”.
Commit
Command: git commit -m “<message>”
Transfers all files from “staging” via a new “commit” into the repository.
Reset
Command: git reset <file> oder git reset <commit>
Removes given files from “staging”.
But you can also use git reset <commit> to set the repository to an older commit and therefore an older version of your software.
Log
Command: git log
Shows the last commits inkl. messages in a list.
Diff
Command: git diff
Shows the difference between the current workspace and the files, that have been added to “staging”. Can also be specifically called for a file git diff <file> to just show the changes in that given file.
Checkout
Command variatens
- git checkout <commit-hash>
- git checkout <filename> <foldername> <other-things>
- git checkout <branch>